New paper published: CiSE journal
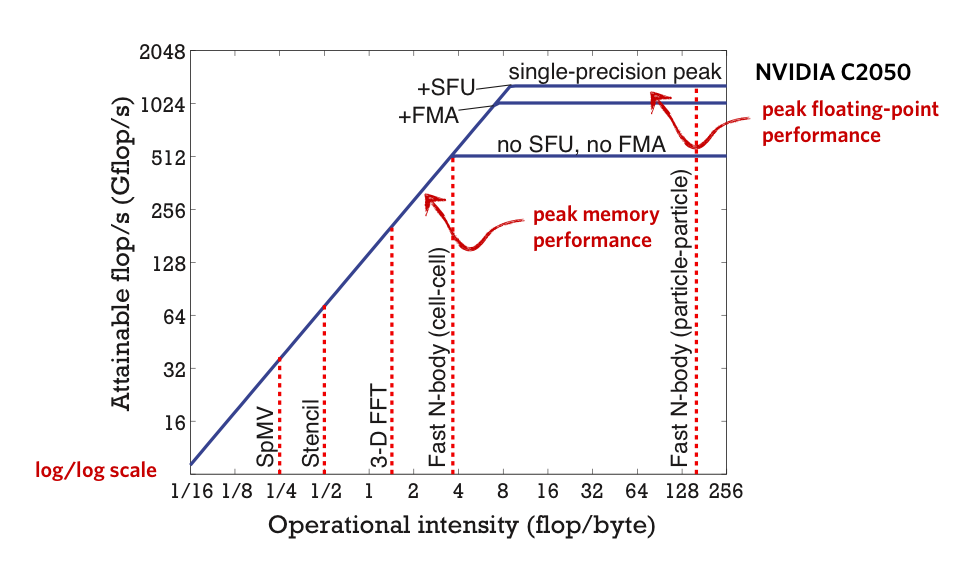
The Roofline model relates floating-point performance, operational performance and memory performance. This model distinctly quantifies the high operational intensity of fast N-body algorithms and reveals their advantage on many-core architectures.
A new paper authored by Rio Yokota and Lorena Barba has appeared (published online 3 Jan. 2012) in Computing in Science and Engineering, the joint publication of the IEEE Computer Society and he American Institute of Physics.
This paper presents a new hybrid treecode/FMM formulation that has been implemented in the ExaFMM code, recently released at the Supercomputing Conference with a poster at the NVIDIA booth. The hybrid method maintains the O(N) complexity of FMM, but is able to perform both cell-cell and cell-particle interactions (i.e., it is both a treecode and an FMM code at the same time).
The method was implemented in the exaFMM code with auto-tuning. This code is able to dynamically choose which type of interaction to perform, according to micro-benchmarks of the kernels: it selects cell-cell, cell-particle, or particle-particle interactions to obtain optimum runtime. This feature is enabled by means of a dual-tree traversal technique, described in this paper (see also the Features section of the exaFMM website).
The paper also discusses the advantage of multipole algorithms on GPU hardware, with the aid of the roofline model to show how it compares with other algorithms. Some of the recent work that is also described includes a many-GPU turbulence calculations on Tsubame 2.0 with 2048 GPUs, which achieved 0.5 petaflop/s in performance.
Reference
- "ExaFMM: An open source library for Fast Multipole Methods aimed towards Exascale systems", L. A. Barba, Rio Yokota. (31 May 2012). 10.6084/m9.figshare.92166
Poster, published on figshare under CC-BY
- "Hierarchical N-body simulations with auto-tuning for heterogeneous systems", Rio Yokota, L. A. Barba. Computing in Science and Engineering (CiSE), 14(3):30–39 (May/June 2012). 10.1109/MCSE.2012.1 // Preprint arXiv:1108.5815
IEEE Computer Society (online 3 Jan. 2012)